Ultra-thin atom layer deposited alumina film enables the precise lifetime control of fully biodegradable electronic devices†
Abstract
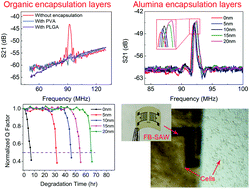
Atomic layer deposited (ALD) ultra-thin alumina film is proposed to control the operational lifetimes of fully biodegradable (FB-) surface sensitive surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices. SAW devices encapsulated with conventional thick organic materials fail to function effectively, while devices with an ultra-thin alumina encapsulation layer (AEL) function normally with high performance. After being subjected to degradation in water, a FB-SAW device with no AEL starts to degrade immediately and fails within 8 h, due to dissolution of the tungsten electrode and piezoelectric material (ZnO). The coating of an ultra-thin AEL on the surfaces prevents SAW devices from undergoing degradation in water and enables SAW devices to perform normally before the AEL is dissolved. The stable operation lifetimes of SAW devices are linearly dependent on the AEL thickness, thus allowing for the design of devices with precisely controlled operational lifetimes and degradation times. The results show that all the materials used could be degraded; also, in vitro cytotoxicity tests indicate that the encapsulated FB-SAW devices are biocompatible, and cells can adhere and proliferate on them normally, demonstrating great potential for broader biodegradable electronic device applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...