Out-of-plane ion transport makes nitrogenated holey graphite a promising high-rate anode for both Li and Na ion batteries†
Abstract
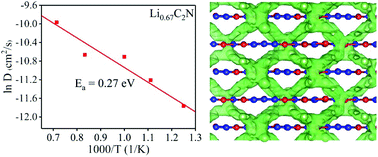
The search for suitable anodes with good performance is a key challenge for rechargeable Li- and Na-ion batteries (LIBs and NIBs). In this work, we adopt first-principles calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the ion transport mechanism and potential of C2N stoichiometric nitrogenated holey graphite (C2N-NHG) as a promising anode material for LIBs and NIBs. Although huge in-plane diffusion barriers for both Li and Na ions restrict the application of the C2N-NHG monolayer as an effective anode, Li and Na ions are found to exhibit facile out-of-plane ion transport in the most stable layered AD stacking C2N-NHG. The fully lithiated and sodiated cases of LiC2N and Na0.67C2N show reversible specific capacities up to 587 mA h g−1 and 353 mA h g−1, low chemical potentials of 0.12 V and 0.25 V, and small volume expansions of 7.16% and 13.54%, respectively. Meanwhile, the out-of-plane collective diffusion reduces Li/Na collective migration barriers to 0.23 eV and 0.18 eV. These findings suggest that AD stacking C2N-NHG, with metallic properties after lithiation and sodiation processes, high specific capacity, low open circuit voltage, small volume expansion, and low collective migration barriers, has the potential to serve as a promising high-rate anode material for LIBs and NIBs with large energy density and power density. The calculations reveal that the novel out-of-plane diffusion behaviour plays a crucial role in Li/Na ion transport in holey layered materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...