A multifunctional liposomal nanoplatform co-delivering hydrophobic and hydrophilic doxorubicin for complete eradication of xenografted tumors†
Abstract
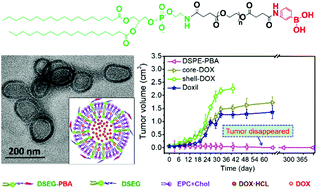
In the war against cancer, tremendous efforts have been made by using a nanoparticle-based anticancer drug system. However, it is still a great challenge to achieve complete cure and eradication of cancer through chemotherapy. Here, we present a new multifunctional liposomal nanoplatform simultaneously loaded with hydrophilic doxorubicin hydrochloride in the aqueous core and hydrophobic debydrochlorination doxorubicin in the lipid bilayer. Compared with the traditional nanoparticle-based drug delivery system, this nanocarrier has three unique functions including a high payload of the same therapeutic agents with different water-solubilities, highly selective delivery of cargos to tumor cells and long-acting time with tumors. An excellent in vitro antitumor potency can be achieved with an IC50 of 0.91 μg mL−1 for this liposome, which is only half the IC50 of free doxorubicin. More importantly, extremely good antitumor efficacy in vivo is achieved since the mean tumor volume of all xenografted tumors is respectively ∼20% and ∼10% of that of the commercial liposomal doxorubicin formulation and the single doxorubicin liposomes on day 17 after being intravenously injected with the liposome nanoformulation 4 times. Moreover, the tumors were completely cured and eradicated on day 60 with no recurrence and the survival rate still remained at 70% after 365 days. Therefore, this multifunctional binary-drug loaded liposome provides a great potential platform for winning the war against cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...