Non-volatile, phase-transition smart gels visually indicating in situ thermal status for sensing applications†
Abstract
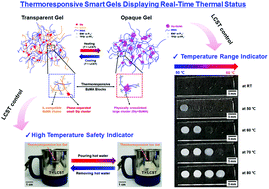
Non-volatile smart gel platforms that change optical properties according to temperature are successfully prepared based on a random copolymer, poly(styrene-ran-benzyl methacrylate-ran-methyl methacrylate) [(P(S-r-BzMA-r-MMA)]. The P(S-r-BzMA-r-MMA) copolymers are judiciously designed to serve as both polymer hosts for a gel, and thermoresponsive materials. In contrast to typical lower critical solution temperature (LCST) or upper critical solution temperature (UCST) systems including sol–gel (or gel–sol) transition, the thermoresponsive gels consisting of the P(S-r-BzMA-r-MMA) and ionic liquids (ILs) maintain an elastic gel-state due to their network structure irrespective of phase transitions. We investigate the effects of the copolymer composition and copolymer/IL ratio on the gel properties. Temperature dependent self-assembly of the gel is revealed using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Thermal response of the gel is examined optically and dynamically. Moreover, we propose a simple method to additionally control the response temperature and the mechanical robustness of the gels by incorporating additional salts. Lastly, we successfully demonstrate practical feasibility of the thermoresponsive gels in high-temperature safety indicators and temperature range indicators, in which the gels visually display in situ thermal status by a change in optical transmittance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...