Excimer ultraviolet-irradiated exfoliated graphite loaded with carbon-coated SnOx small nanoparticles as advanced anodes for high-rate-capacity lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
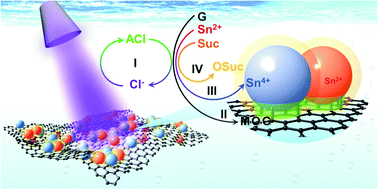
This paper reports a fast and efficient excimer ultraviolet (EUV) radiation method to prepare carbon-coated mixed tin oxide-loaded exfoliated graphite (SnOx@C-G) nanocomposites. The SnOx small nanoparticles (SNPs) are isolated using oxidized sucrose and uniformly deposited onto mildly oxidized exfoliated graphite during the 20-minute EUV radiation process. XPS and ESR analyses suggest the existence of abundant oxygen vacancies in the SnOx SNPs. The electrochemical kinetics of SnOx@C-G, which are determined by in situ electrochemical impedance analysis, demonstrated a high reversible capacity of approximately 740 mA h g−1 after 250 cycles at a current density of 1.6 A g−1, and an impressive reversible rate performance exceeding 450 mA h g−1 can be obtained even at a high current density of 3.2 A g−1 when applied as an anode for lithium storage. This improved cycling stability and rate capability benefit from the carbon coating, which not only buffers the volume change of SnOx SNPs but also provides a path for electron transport on the surface of the SnOx SNPs during the electrochemical process. Furthermore, the oxygen vacancies in SnOx SNPs result in a large capacitive contribution to capacity. The EUV radiation method used to synthesize SnOx@C-graphite nanosheets is universally applicable to prepare a high-performance SNPs/carbon-based anode for lithium-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...