Universal description of heating-induced reshaping preference of core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles†
Abstract
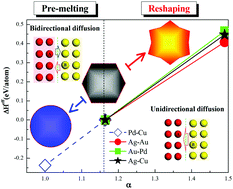
To achieve universal description of the reshaping process of core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles, we combined the tight-binding Ising Hamiltonian model with molecular dynamic simulations to propose a general theoretical model at the atomic scale while considering the temperature, bond energy, atomic size, and surface energy effects. Based on this model, we can quantitatively analyze the tendency of core–shell structured bimetallic nanoparticles toward the reshaping phenomenon upon heating. By rapidly screening 196 types of bimetallic nanoparticles (containing transition metal elements from VIII to IIB groups in the fourth, fifth, and sixth rows of the periodic table), we identified forty-four kinds of bimetallic nanoparticles with reshaping tendency upon heating, which was validated by molecular dynamic simulations and available experimental results. With increasing temperature, the bimetallic nanoparticles with reshaping preference were transformed from an icosahedron to a star-like shape. In contrast, the structure of bimetallic nanoparticles without reshaping preference was transformed from an icosahedron to a sphere shape, which is usually considered to be the normal pre-melting phenomenon. Further structural analysis indicated that the reshaping of bimetallic nanoparticles could be ascribed to different diffusion mechanisms, where a dominant unidirectional mechanism leads to reshaped bimetallic nanoparticles and a bidirectional diffusion mechanism results in no-reshaped bimetallic nanoparticles. This study provides a deep insight into the origin of reshaping in bimetallic nanoparticles, and it may stimulate extensive studies on engineering bimetallic nanoparticles to switch on/off reshaping upon heating, for example, by modifying the structures, atomic arrangement or composites of bimetallic systems in future.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...