A general gelation strategy for 1D nanowires: dynamically stable functional gels for 3D printing flexible electronics†
Abstract
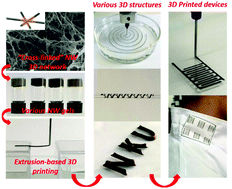
3D printing of functional inorganic nanowires has been accomplished using extruded nanowire-based inks obtained by incorporating nanofillers into polymeric matrices or thickeners. However, the presence of inactive additives poses a critical challenge for fully realizing the functionality of the nanowires in the printed structures, which remains a fundamental hurdle to overcome. Here, to construct 3D-printed electronics with high performance, we developed a versatile gelation strategy to obtain thixotropic nanowire gels through formation of dynamically stable 3D networks using small amounts of flexible, water-soluble and single-layer 2D nanosheets, such as graphene oxide and MXene, as physical cross-linkers. The nanosheets can knot-tie and stabilize the nanowire junctions in the aqueous suspension, leading to the formation of stable and thixotropic gels with viscosities up to ∼80 000 Pa s at 0.01 s−1 in the absence of polymer thickener. Gels of varioius metallic and semiconductive nanowires have been successfully prepared and printed into 3D and self-supported architectures via extrusion-based 3D-printing. The synergism of nanowires and nanosheets not only conquers the restraints of harsh post-treatments to remove additives after printing, but also maximizes the functionality of the nanowires in the printed architectures. The printed 3D structures solidified by ambient drying, coagulation, or freeze-drying exhibit remarkable functionalities. For example, the electrical conductivity of the 3D-printed silver nanowire-based architectures can reach 40 000 S cm−1. The feasibility of these functional nanowire gels was demonstrated by fabricating a series of printed flexible electronics via extrusion-based 3D-printing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...