Artificial lithium fluoride surface coating on silicon negative electrodes for the inhibition of electrolyte decomposition in lithium-ion batteries: visualization of a solid electrolyte interphase using in situ AFM†
Abstract
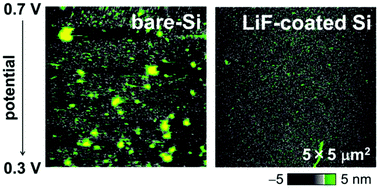
The solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), which is a surface layer formed on the negative electrode, plays an important role in inhibiting the reductive decomposition of the electrolyte solution in a lithium-ion battery. However, it has not been understood well which components are important for the SEI to prevent the electrolyte decomposition. Lithium fluoride (LiF), as an artificial SEI, was formed on an amorphous-Si thin film by physical vapor deposition. Changes in the surface morphology of the Si electrode with potential sweeping were investigated using in situ atomic force microscopy (AFM). Although large amounts of non-uniform surface deposits that originate from electrolyte decomposition emerged on the bare Si-film electrode during the first lithiation process, few surface deposits were observed on the LiF-coated Si-film electrode even after two cycles in an ethylene carbonate-based electrolyte solution without additives. It is clear that LiF is a required SEI component that inhibits electrolyte decomposition on Si negative electrodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
