Unraveling the solvent induced welding of silver nanowires for high performance flexible transparent electrodes†
Abstract
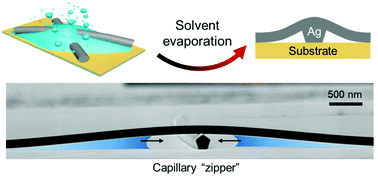
A solution processed metal nanowire network is a promising flexible transparent electrode to replace brittle metal oxides for printable optoelectronics applications, but suffers from the issue of pseudo contact between nanowires. Herein, using volatile solvent mists as a powerful “zipper”, we demonstrate a simple and rapid method to effectively weld silver nanowires, which dramatically improves the conductivity and robustness of the silver nanowire network based flexible transparent electrodes. We reveal that for a stacked network structure, the unique wedge-shaped nanogaps between the long nanowires and substrate provide a strong capillary force during solvent evaporation, which is much larger than that between zero-dimensional nanoparticles and gives a decisive contribution for nanowire junction welding, and this nanowire–substrate interplay force is positively related to the wettability of the substrate. At the same time, the dissolution–reprecipitation of the capping agent on the silver nanowire surface as the natural adhesive can fix the network on the substrate tightly, which enhances the robustness of the network. Our approach solves two key issues in solution-processed transparent electrodes in one simple step, and is compatible with various mild solution-processed optoelectronic devices, especially those containing heat-sensitive or chemical-sensitive materials. Moreover, a new type of invisible infrared encryption display is demonstrated based on this approach.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...