Novel protein–lipid composite nanoparticles with an inner aqueous compartment as delivery systems of hydrophilic nutraceutical compounds†
Abstract
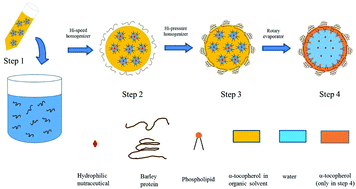
Food protein and lipid based nanoparticles have attracted recent interest as a means of delivering nutraceuticals. Nanoparticle encapsulation of nutraceuticals faces challenges to overcome for it to be readily applied in the food industry, such as low encapsulation efficiency for hydrophilic compounds and poor stability once in the gastrointestinal tract. This research introduces a new protein–lipid composite nanoparticle with a three-layered structure (a barley protein layer, α-tocopherol layer and phospholipid layer) and an inner aqueous compartment to load hydrophilic nutraceuticals. This delivery system showed efficient encapsulation of vitamin B12 (69%) and controlled release behavior in simulated gastrointestinal media. An in vitro cell evaluation demonstrated that nanoparticles could internalize into Caco-2 cells via energy-dependent endocytosis and significantly increase the uptake and transport efficiency of vitamin B12 in this model. In vivo, the developed vitamin B12 loaded nanoparticle showed increased serum vitamin B12 levels upon oral administration and reduced the methylmalonic acid level more efficiently than the free form in rats. A 14-day in vivo toxicity study showed no evidence of toxicity in rats implying the safety of the developed nanoparticles in long term use. Overall, the results of this study show the great potential of the developed nanoparticles in increasing the absorption of vitamin B12 upon oral administration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...