Enhanced delivery of siRNA to triple negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through functionalizing lipid-coated calcium phosphate nanoparticles with dual target ligands†
Abstract
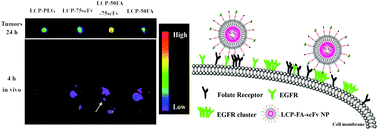
The conjugation of ligands to nanoparticle platforms for the target delivery of therapeutic agents to the tumor tissue is one of the promising anti-cancer strategies. However, conventional nanoparticle platforms are not so effective in terms of the selectivity and transfection efficiency. In this study, we designed and developed a dual-target drug/gene delivery system based on lipid-coated calcium phosphate (LCP) nanoparticles (NPs) for significantly enhanced siRNA cellular uptake and transfection efficiency. LCP NPs loaded with therapeutic siRNA were conjugated with a controlled number of folic acid and/or EGFR-specific single chain fragment antibody (ABX-EGF scFv). The uptake of ABX-EGF scFv-modified (LCP-scFv) and folic acid-modified LCP NPs (LCP-FA) by human breast tumor cells (MDA-MB-468) was significantly higher with an optimal ligand density on each NP surface (LCP-125scFv and LCP-100FA). Co-conjugation with sub-optimal dual ligands (50 FA and 75 ABX-EGF scFv) per LCP NP (LCP-50FA-75scFv) further enhanced the cellular uptake. More significantly, much more NPs were delivered to the MDA-MB-468 tumor tissue in the nude mouse model when LCP-50FA-75scFv NPs were used. Therefore, the new dual-ligand LCP NPs may be a valuable targeting system for human breast cancer diagnosis and therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...