In situ growth of gold nanoparticles on Hg2+-binding M13 phages for mercury sensing†
Abstract
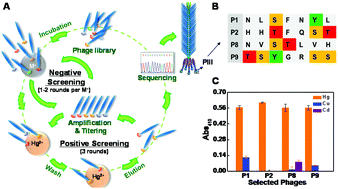
Mercury poses a serious threat to human health and the ecosystem. Its pollution is still prevalent in developing areas, which calls for the development of a simple on-site method for Hg2+ detection. Plasmonic nanosensors for mercury, especially those based on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), have been increasingly developed due to the flourish of nanotechnology in the last decade. However, the limitation on either selectivity or stability hindered their practical applications. Herein, by taking advantage of the unique optical properties of AuNPs and the versatility of M13 phages, a novel Hg2+ sensing strategy is proposed. AuNPs grew in situ on the surface of Hg2+-binding M13 phages at room temperature and the resulting AuNP-phage networks were directly used for mercury sensing. Hg2+ was selectively captured by M13 phages indwelling in the networks and gathered around AuNPs, followed by the reduction into Hg(0) and deposition on the AuNP surfaces, wherein it resulted in a blue shift of the SPR band of AuNPs and an increase in the absorbance. An LOD of 8 × 10−8 mol L−1 was achieved based on the quantification of the absorption ratio of AuNPs at 525 and 650 nm. As the Hg2+ recognition was double guaranteed by the capture of Hg2+-binding phages as well as the unique affinity between mercury and gold, the sensing system showed a high selectivity and a superior interference tolerance capability, facilitating its practical applications in environmental water bodies without deterioration of the sensing performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...