Fullerenol nanoparticles suppress RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting differentiation and maturation†
Abstract
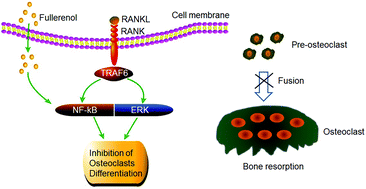
Bone health requires regulation of homeostatic equilibrium between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The over-activation of osteoclasts can disrupt bone metabolism, resulting in osteoporosis and other bone-loss diseases. Fullerenol, a polyhydroxy derivative of fullerene, exhibits excellent biocompatibility. Here we show that fullerenol nanoparticles exert two functions: inhibition of osteoclastic differentiation and blockage of pre-osteoclast fusion to restructure osteoclast maturation and function. Experimentally, the nanoparticles reduced pre-osteoclast migration and inhibited ruffled border formation to block their maturation. In addition, fullerenol dose-dependently restricted the differentiation of bone marrow macrophage cells (BMMs) to form osteoclasts following treatment with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-κB (RANKL) to activate NF-κB and mitogen activating protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. It is possible that the very small size of fullerenol allows it to directly cross the cellular membrane to access the cytoplasm and regulate osteoclastogenesis from BMMs. Our results suggest that fullerenol could be used to treat bone-loss diseases such as osteoporosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...