A photovoltaic self-powered gas sensor based on a single-walled carbon nanotube/Si heterojunction†
Abstract
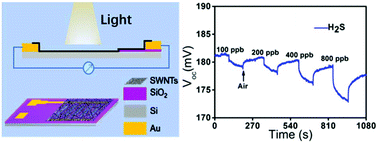
We present a novel photovoltaic self-powered gas sensor based on a p-type single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) and n-type silicon (n-Si) heterojunction. The energy from visible light suffices to drive the device owing to a built-in electric field (BEF) induced by the differences between the Fermi levels of SWNTs and n-Si.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...