Optimization of the Ag/PCBM interface by a rhodamine interlayer to enhance the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
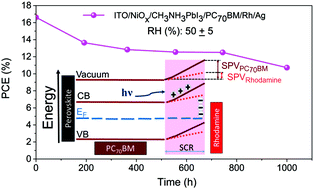
Effective control of the interface between the metal cathode and the electron transport layer (ETL) is critical for achieving high performance p–i–n planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells (PSCs). Several organic molecules have been explored as interlayers between the silver (Ag) electrode and the ETL for the improvement in the photovoltaic conversion efficiency (PCE) of p–i–n planar PSCs. However, the role of these organic molecules in the charge transfer at the metal/ETL interface and the chemical degradation processes of PSCs has not yet been fully understood. In this work, we systematically explore the effects of the interfacial modification of the Ag/ETL interface on PSCs using rhodamine 101 as a model molecule. By the insertion of rhodamine 101 as an interlayer between Ag and fullerene derivatives (PC60BM and PC70BM) ETLs improve the PCE as well as the stability of p–i–n planar PSCs. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterization reveals that rhodamine passivates the defects at the PCBM layer and reduces the band bending at the PCBM surface. In consequence, charge transfer from the PCBM towards the Ag electrode is enhanced leading to an increased fill factor (FF) resulting in a PCE up to 16.6%. Moreover, rhodamine acts as a permeation barrier hindering the penetration of moisture towards the perovskite layer as well as preventing the chemical interaction of perovskite with the Ag electrode. Interestingly, the work function of the metal cathode remains more stable due to the rhodamine incorporation. Consequently, a better alignment between the quasi-Fermi level of PCBM and the Ag work function is achieved minimizing the energy barrier for charge extraction. This work contributes to reveal the relevance of proper interfacial engineering at the metal-cathode/organic-semiconductor interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...