Periodic oscillation of ion conduction of nanofluidic diodes using a chemical oscillator†
Abstract
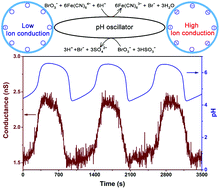
Periodic ion-conduction oscillation of biological ion channels in a living system is essential for numerous life processes. Here we report an oscillatory nanofluidic system that can self-regulate its ion-conduction states under constant conditions. The oscillatory nanofluidic system is constructed by integrating a chemical oscillator into an artificial single nanochannel system. Oscillating chemical reactions of the pH oscillator carried out inside the nanochannel are used to switch the surface properties of the channel between highly and lowly charged states, thus realizing an autonomous, continuous and periodic oscillation of the ion conductance of the channel between high and low ion-conduction states. The ion-conduction switching is characterized by the periodic ion current oscillation of the nanochannel measured under constant conditions. The oscillation period of the nanofluidic devices decreased gradually with increasing the working temperature. This study is a potential step toward the ability to directly convert chemical energy to ion-conduction oscillation in nanofluidics. On the basis of these findings, we believe that a variety of artificial oscillatory nanofluidic systems will be achieved in future by integrating artificial functional nanochannels with diverse oscillating chemical reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...