A wearable strain sensor based on a carbonized nano-sponge/silicone composite for human motion detection†
Abstract
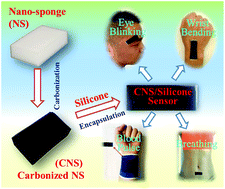
Melamine sponge, also known as nano-sponge, is widely used as an abrasive cleaner in our daily life. In this work, the fabrication of a wearable strain sensor for human motion detection is first demonstrated with a commercially available nano-sponge as a starting material. The key resistance sensitive material in the wearable strain sensor is obtained by the encapsulation of a carbonized nano-sponge (CNS) with silicone resin. The as-fabricated CNS/silicone sensor is highly sensitive to strain with a maximum gauge factor of 18.42. In addition, the CNS/silicone sensor exhibits a fast and reliable response to various cyclic loading within a strain range of 0–15% and a loading frequency range of 0.01–1 Hz. Finally, the CNS/silicone sensor as a wearable device for human motion detection including joint motion, eye blinking, blood pulse and breathing is demonstrated by attaching the sensor to the corresponding parts of the human body. In consideration of the simple fabrication technique, low material cost and excellent strain sensing performance, the CNS/silicone sensor is believed to have great potential in the next-generation of wearable devices for human motion detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...