Nanoscale patterning of biopolymers for functional biosurfaces and controlled drug release†
Abstract
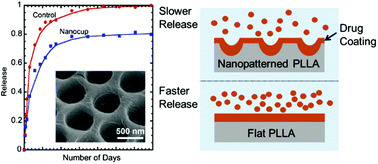
We compare the rates of drug release from nanopatterned and flat biodegradable polymer surfaces, and observe significantly lower release rates from the nanopatterned surfaces. Specifically, we nanopattern poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA), a biodegradable polymer frequently used for fabricating drug-eluting coronary stents, through microtransfer molding and solvent casting and investigate the nanopattern's impact on the release of sirolimus, an immunosuppressant agent, coated on the PLLA surface using high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. We find that PLLA surfaces nanopatterned with 750 nm-pitch nanocup or nanocone arrays exhibit drug release rates significantly lower (25–30%) than that of the flat surface, which is counter-intuitive given the nanopattern-induced increase in their surface areas. Based on diffusion and meniscus curvature minimization analyses, we attribute the decreased drug release rate to the incomplete wetting of the nanopatterned surface. These results provide new insights on how the surface nanopatterning of biomaterials can functionalize the surface and tailor the release kinetics of therapeutic agents coated on it for controlled drug elution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...