Free-standing iridium and rhodium-based hierarchically-coiled ultrathin nanosheets for highly selective reduction of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene under ambient conditions†
Abstract
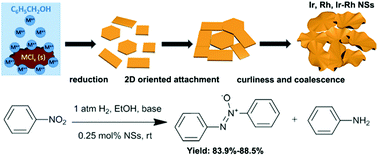
The fabrication of atom-layered two dimensional (2D) noble metal nanosheets (NSs) in a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure is of broad scientific and technological importance, yet this remains a challenge due to the intrinsic cubic symmetry and high surface energy of fcc noble metals. Herein, we report a solid–liquid interface mediated 2D growth method towards the synthesis of hierarchically-coiled ultrathin Ir NSs (thickness <2 nm) and Rh NSs (0.8 nm thick), and bimetallic Ir–Rh NSs (1.2 nm thick) and Pt–Rh NSs (1.2 nm thick) using the benzyl alcohol solvothermal approach. The formation of NSs was attributed to the 2D oriented attachment of tiny seeds through the lateral growth stemming from the abundant defect sites of the seeds produced in the heterogeneous system. The free-standing Ir NSs, Rh NSs and Ir–Rh NSs exhibited high selectivities (from 83.9% to 88.5%) towards the selective reduction of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene in ethanol at room temperature with 1 atm of hydrogen, because the condensation step of nitrosobenzene (PhNO) and phenylhydroxylamine (PhNHOH) was more exothermic than the dissociation step of Ph-NHOH on the (111) facets of the NSs under alkaline conditions, as indicated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...