An amphiphilic graft copolymer-based nanoparticle platform for reduction-responsive anticancer and antimalarial drug delivery†
Abstract
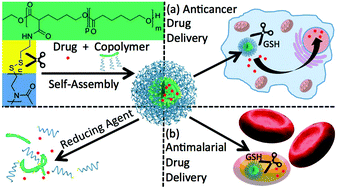
Medical applications of anticancer and antimalarial drugs often suffer from low aqueous solubility, high systemic toxicity, and metabolic instability. Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems provide means of solving these problems at once. Herein, we present such a smart nanoparticle platform based on self-assembled, reduction-responsive amphiphilic graft copolymers, which were successfully synthesized through thiol–disulfide exchange reaction between thiolated hydrophilic block and pyridyl disulfide functionalized hydrophobic block. These amphiphilic graft copolymers self-assembled into nanoparticles with mean diameters of about 30–50 nm and readily incorporated hydrophobic guest molecules. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) was used to study nanoparticle stability and triggered release of a model compound in detail. Long-term colloidal stability and model compound retention within the nanoparticles was found when analyzed in cell media at body temperature. In contrast, rapid, complete reduction-triggered disassembly and model compound release was achieved within a physiological reducing environment. The synthesized copolymers revealed no intrinsic cellular toxicity up to 1 mg mL−1. Drug-loaded reduction-sensitive nanoparticles delivered a hydrophobic model anticancer drug (doxorubicin, DOX) to cancer cells (HeLa cells) and an experimental, metabolically unstable antimalarial drug (the serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) inhibitor (±)-1) to Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells (iRBCs), with higher efficacy compared to similar, non-sensitive drug-loaded nanoparticles. These responsive copolymer-based nanoparticles represent a promising candidate as smart nanocarrier platform for various drugs to be applied to different diseases, due to the biocompatibility and biodegradability of the hydrophobic block, and the protein-repellent hydrophilic block.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...