Zirconium–metalloporphyrin frameworks as a three-in-one platform possessing oxygen nanocage, electron media, and bonding site for electrochemiluminescence protein kinase activity assay†
Abstract
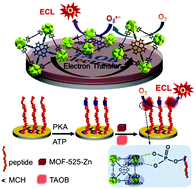
A Zr-based metal–organic framework with zinc tetrakis(carboxyphenyl)-porphyrin (ZnTCPP) groups (MOF-525-Zn) was utilized to develop a novel electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor for highly sensitive protein kinase activity assay. In this work, in terms of ECL measurements and cyclic voltammetry, the cathodic ECL behaviors of MOF-525-Zn in aqueous media were thoroughly investigated for the first time. The photoelectric active groups ZnTCPP on the MOF-525-Zn frameworks could promote the generation of singlet oxygen (1O2) via a series of electrochemical and chemical reactions, resulting in a strong and stable red irradiation at 634 nm. Additionally, the surfactant tetraoctylammonium bromide (TOAB) further facilitated dissolved oxygen to interact with the active sites ZnTCPP of MOF-525-Zn. Furthermore, the inorganic Zr–O clusters of MOF-525-Zn were simultaneously served as the recognition sites of phosphate groups. And then, an ultrasensitive ECL sensor was proposed for protein kinase A (PKA) activity detection with a linear range from 0.01 to 20 U mL−1 and a sensitive detection limit of 0.005 U mL−1. This biosensor can also be applied for quantitative kinase inhibitor screening. Finally, it exhibits good performance with high stability and acceptable fabrication reproducibility, which provide a valuable strategy for clinic diagnostics and therapeutics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...