Charge transfer and surface defect healing within ZnO nanoparticle decorated graphene hybrid materials†
Abstract
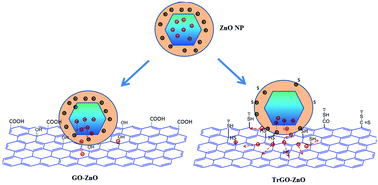
To harness the unique properties of graphene and ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) for novel applications, the development of graphene–ZnO nanoparticle hybrid materials has attracted great attention and is the subject of ongoing research. For this contribution, graphene-oxide–ZnO (GO–ZnO) and thiol-functionalized reduced graphene oxide–ZnO (TrGO–ZnO) nanohybrid materials were prepared by novel self-assembly processes. Based on electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and photoluminescence (PL) investigations on bare ZnO NPs, GO–ZnO and TrGO–ZnO hybrid materials, we found that several physical phenomena were occurring when ZnO NPs were hybridized with GO and TrGO. The electrons trapped in Zn vacancy defects (VZn−) within the core of ZnO NPs vanished by transfer to GO and TrGO in the hybrid materials, thus leading to the disappearance of the core signals in the EPR spectra of ZnO NPs. The thiol groups of TrGO and sulfur can effectively “heal” the oxygen vacancy (VO+) related surface defects of ZnO NPs while oxygen-containing functionalities have low healing ability at a synthesis temperature of 100 °C. Photoexcited electron transfer from the conduction band of ZnO NPs to graphene leads to photoluminescence (PL) quenching of near band gap emission (NBE) of both GO–ZnO and TrGO–ZnO. Simultaneously, electron transfer from graphene to defect states of ZnO NPs is the origin of enhanced green defect emission from GO–ZnO. This observation is consistent with the energy level diagram model of hybrid materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...