Assembling patchy nanorods with spheres: limitations imposed by colloidal interactions†
Abstract
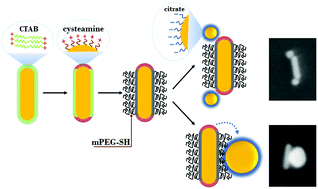
For gold nanorods the intrinsic shape-anisotropy offers the prospect of anisotropic assembly, provided that their region-selective surface modification can be realized. Here we developed nanorods with a patchy surface chemistry, featuring positively charged molecules in the tip region and polymer molecules at the sides by careful control of molecule concentrations during ligand exchange. When these patchy nanorods are assembled with small negatively charged spherical particles, electric double layer interaction can direct the assembly of two nanospheres at the opposite ends of the nanorods. The PEG chains promote the selectivity of the procedure. As the size of the nanospheres increases, they start to shift towards the side of the nanorod due to increased van der Waals interaction. When the relative size of the nanospheres is even larger, only a single nanosphere is assembled, but instead of the tip region, they are attached to the side of the nanorods. The apparent cross-over of the region-selectivity can be interpreted in terms of colloidal interactions, i.e. the second spherical particle is excluded due to nanosphere–nanosphere electric double layer repulsion, while the large vdW attraction results in a side positioning of the single adsorbed spherical particle. The results underline the importance of absolute values of the different interaction strengths and length scales in the programmed assembly of patchy nanoscale building blocks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...