Ultrafast direct fabrication of flexible substrate-supported designer plasmonic nanoarrays†
Abstract
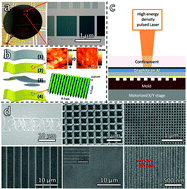
Fabrication of plasmonic nanostructures has been an important topic for their potential applications in photonic and optoelectronic devices. Among plasmonic materials, gold is one of the most promising materials due to its low ohmic loss at optical frequencies and high oxidation resistance. However, there are two major bottlenecks for its industrial applications: (1) the need for large-scale fabrication technology for high-precision plasmonic nanostructures; and (2) the need to integrate the plasmonic nanostructures on various substrates. While conventional top-down approaches involve high cost and give low throughput, bottom-up approaches suffer from irreproducibility and low precision. Herein, we report laser shock induced direct imprinting of large-area plasmonic nanostructures from physical vapor deposited (PVD) gold thin film on a flexible commercial free-standing aluminum foil. Among the important characteristics of the laser-shock direct imprinting is their unique capabilities to reproducibly deliver designer plasmonic nanostructures with extreme precision and in an ultrafast manner. Excellent size tunability (from several μm down to 15 nm) has been achieved by varying mold dimensions and laser parameters. The physical mechanism of the hybrid film imprinting is elaborated by finite element modeling. A mechanical robustness test of the hybrid film validates a significantly improved interfacial contact between gold arrays and the underlying substrate. The strong optical field enhancement was realized in the large-area fabricated engineered gold nanostructures. Low concentration molecular sensing was investigated employing the fabricated structures as surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates. The ability to ultrafast direct imprint plasmonic nanoarrays on a flexible substrate at multiscale is a critical step towards roll-to-roll manufacturing of multi-functional devices which is poised to inspire several emerging applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...