Zinc oxide nanorod assisted rapid single-step process for the conversion of electrospun poly(acrylonitrile) nanofibers to carbon nanofibers with a high graphitic content†
Abstract
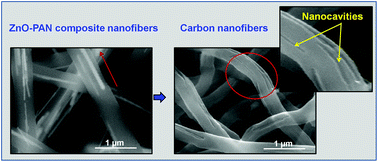
The effect of incorporation of rigid zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostructures on carbonization behavior of electrospun special acrylic fiber grade poly(acrylonitrile) (PAN-SAF) nanofibers was investigated. ZnO nanorods with high aspect ratios were incorporated into a PAN-N,N-dimethylformamide system and the composite nanofibers reinforced with aligned ZnO rods up to 50 wt% were successfully electrospun, and subsequently, carbonized. The morphology and the structural analysis of the resultant carbon nanofibers revealed that the rigid ZnO nanorods, present inside the nanofibers, possibly acted as scaffolds (temporary support structures) for immobilization of polymer chains and assisted in uniform heat distribution. This facilitated rapid and efficient conversion of the polymer structure to the ladder, and subsequently, the graphitized structure. At the end of the process, the ZnO nanorods were found to completely separate from the carbonized fibers yielding pure carbon nanofibers with a high graphitic content and surface area. The approach could be used to eliminate the slow, energy intensive stabilization step and achieve fast conversion of randomly laid carbon nanofiber webs in a single step to carbon nanofibers without the application of external tension or internal templates usually employed to achieve a high graphitic content in such systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...