Host–guest interaction induced supramolecular amphiphilic star architecture and uniform nanovesicle formation for anticancer drug delivery†
Abstract
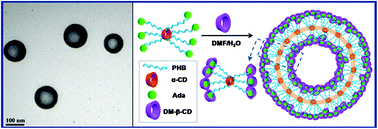
A star polymer of poly[(R,S)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB) with adamantyl end-terminals extended from an α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) core is designed. It subsequently self-assembles to form controllable and uniform nanovesicles induced by host–guest interactions between heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-CD and the adamantyl ends. The nanovesicles are suitable for loading and intracellular delivery of the anticancer drug doxorubicin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...