Thermal conductivities of single- and multi-layer phosphorene: a molecular dynamics study
Abstract
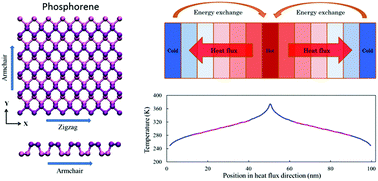
As a new two-dimensional (2D) material, phosphorene has drawn growing attention owing to its novel electronic properties, such as layer-dependent direct bandgaps and high carrier mobility. Herein we investigate the in-plane and cross-plane thermal conductivities of single- and multi-layer phosphorene, focusing on geometrical (sample size, orientation and layer number) and strain (compression and tension) effects. A strong anisotropy is found in the in-plane thermal conductivity with its value along the zigzag direction being much higher than that along the armchair direction. Interestingly, the in-plane thermal conductivity of multi-layer phosphorene is insensitive to the layer number, which is in strong contrast to that of graphene where the interlayer interactions strongly influence the thermal transport. Surprisingly, tensile strain leads to an anomalous increase in the in-plane thermal conductivity of phosphorene, in particular in the armchair direction. Both the in-plane and cross-plane thermal conductivities can be modulated by external strain; however, the strain modulation along the cross-plane direction is more effective and thus more tunable than that along the in-plane direction. Our findings here are of great importance for the thermal management in phosphorene-based nanoelectronic devices and for thermoelectric applications of phosphorene.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...