The effect of nanocrystalline silicon host on magnetic properties of encapsulated iron oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
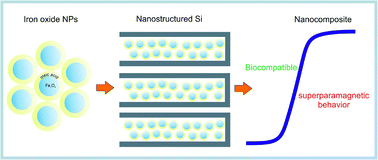
The purpose of this work is a detailed comparison of the fundamental magnetic properties of nanocomposite systems consisting of Fe3O4 nanoparticle-loaded porous silicon as well as silicon nanotubes. Such composite structures are of potential merit in the area of magnetically guided drug delivery. For magnetic systems to be utilized in biomedical applications, there are certain magnetic properties that must be fulfilled. Therefore magnetic properties of embedded Fe3O4-nanoparticles in these nanostructured silicon host matrices, porous silicon and silicon nanotubes, are investigated. Temperature-dependent magnetic investigations have been carried out for four types of iron oxide particle sizes (4, 5, 8 and 10 nm). The silicon host, in interplay with the iron oxide nanoparticle size, plays a sensitive role. It is shown that Fe3O4 loaded porous silicon and SiNTs differ significantly in their magnetic behavior, especially the transition between superparamagnetic behavior and blocked state, due to host morphology-dependent magnetic interactions. Importantly, it is found that all investigated samples meet the magnetic precondition of possible biomedical applications of exhibiting a negligible magnetic remanence at room temperature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...