Metal–insulator crossover in multilayered MoS2†
Abstract
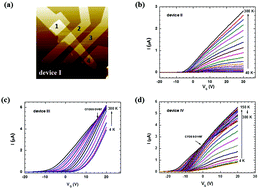
The temperature dependence of electrical transport properties was investigated for multilayered MoS2 field effect transistor devices with thicknesses of 3–22 nm. Some devices showed typical n-type semiconducting behavior, while others exhibited metal–insulator crossover (MIC) from metallic to insulating conduction at finite temperatures. The latter effect occurred near zero gate voltage or at high positive gate voltages. Analysis of Raman spectroscopy revealed the key difference that devices with MIC have a metallic 1T phase as well as a semiconducting 2H phase, whereas devices without the MIC did not have a metallic 1T phase. These results suggest that the metallic 1T phase may contribute to inducing the MIC.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...