Nitrogen-fluorine co-doped titania inverse opals for enhanced solar light driven photocatalysis
Abstract
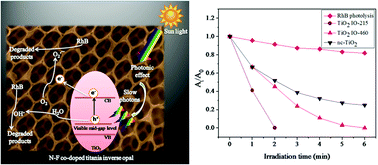
Three dimensionally ordered nitrogen-fluorine (N–F) co-doped TiO2 inverse opals (IOs) were fabricated by templating with polystyrene (PS) colloidal photonic crystals (CPCs) by infiltration. During preparation, the TiO2 precursor was treated with a mixture of nitric acid and trifluoroacetic acid to facilitate N–F co-doping into the TiO2 lattice. Enhanced solar light absorption was observed in the samples as a consequence of the red shift in the electronic band gap of TiO2 due to N–F co-doping. The photonic band gap (PBG) of these TiO2 IO films was tuned by varying the sphere size of the PS CPC templates. The as-prepared N–F co-doped TiO2 IO films were used as photocatalysts for the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) dye under solar light irradiation. A significant enhancement in the photocatalytic activity was observed in N–F co-doped TiO2 IO films prepared using PS spheres of 215 nm as a template, with the red edge of the PBG closer to the electronic band gap (EBG) of TiO2. 100% of the dye molecules were degraded within 2 minutes under direct solar irradiation, which is one of the fastest reaction times ever reported for RhB degradation in the presence of TiO2 photocatalysts. The N–F co-doped TiO2 IO film prepared using PS of 460 nm with its PBG centered at 695 nm also showed good photocatalytic activity. It was found that the IO films displayed improved photocatalytic activity in comparison to ordinary nanocrystalline (nc)-TiO2 films. The enhancement could be attributed to the bandgap scattering effect and the slow photon effect, leading to a significant improvement in solar light harvesting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...