Strong quantum confinement effect and reduced Fröhlich exciton–phonon coupling in ZnO quantum dots embedded inside a SiO2 matrix
Abstract
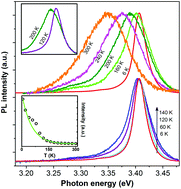
ZnO quantum dots (QDs) embedded in an amorphous SiO2 matrix were examined in depth by using variable-temperature photoluminescence (PL) and optical reflectance spectroscopies. Compared with ZnO bulk crystals, ZnO quantum dots with an average size of 4 nm exhibit a strong quantum confinement effect, evidenced by a large blue shift in both PL and reflectance peaks of excitons. More interestingly, a remarkably reduced long-range Fröhlich interaction was revealed in ZnO QDs. These fascinating effects may make ZnO QDs a very appealing system in the fields of optoelectronics and others.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...