Controllable synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanospheres and Fe–N/carbon nanospheres as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts†
Abstract
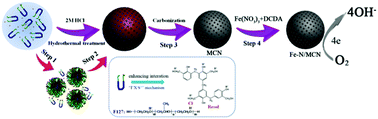
The synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanospheres (MCNs), especially with diameters below 200 nm remains a great challenge due to weak interactions between the carbon precursors and soft templates, as well as the uncontrollable cross-linking rate of carbon precursors. Herein, we demonstrate a simple acid-assisted, hydrothermal synthesis approach to synthesizing such uniform MCNs with well controlled diameters ranging from 20 to 150 nm under highly acidic conditions (2 M HCl). Both the carbon precursor and the template are partly protonated under such conditions and show additional Coulombic interactions with chloride ions (acts as mediators). This kind of enhanced interaction is similar to that of the “I+X−S+” mechanism in the synthesis of mesoporous metal oxide, which can effectively retard the cross-linking rate of resol molecules and avoid macroscopic phase separation during the hydrothermal synthesis. Due to their uniform spherical morphology, small diameter, and high surface areas, MCNs can be modified with Fe and N species via impregnation of cheap precursors (ferric nitrate and dicyandiamide), which are further converted into nonprecious electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. The resulting Fe–N/MCNs exhibit high catalytic activities, long-term stability and improved methanol tolerance under alkaline conditions, which can be potentially used in direct methanol fuel cells and metal-air batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...