Evolution, kinetics, energetics, and environmental factors of graphene degradation on silicon dioxide
Abstract
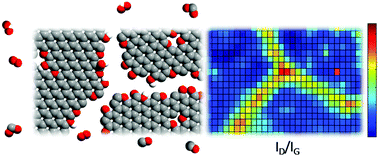
Recent studies have qualitatively shown that the oxidative stability of monolayer graphene integrated on oxides is relatively poor. Here, the evolution, kinetics, and energetics of this degradation are quantified. Specifically, the deterioration of graphene on SiO2 is studied in grain interiors and at grain boundaries in ambient air, dry air and nitrogen between 473 and 673 K, using spatially and temporally resolved in situ Raman spectroscopy in addition to electron microscopy and charge transport measurements. The grain interiors of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene monolayers oxidize with an activation energy of 0.63 ± 0.05 eV in ambient air (15 000 ppm H2O). This energy increases to 1.85 ± 0.17 eV in dry air, whereas degradation is immeasurable in nitrogen and for multilayers even in ambient air. Gasification at grain boundaries in a CVD monolayer proceeds at a rate of (1.08 ± 0.02) × 10−1 nm s−1 at 673 K with an activation energy EA = 1.14 ± 0.10 eV in ambient air. The more facile degradation of the monolayer grain interiors in ambient air indicates the role of the substrate in decreasing the stability against oxidation. The electrical transport mobility decays with an activation rate similar to that of grain interiors. These results can be used to quantitatively predict graphene oxidation and gasification on SiO2 in different environments and temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...