Uniform 2 nm gold nanoparticles supported on iron oxides as active catalysts for CO oxidation reaction: structure–activity relationship
Abstract
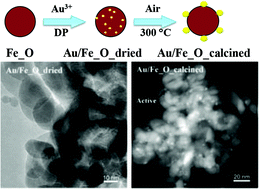
Uniform Au nanoparticles (∼2 nm) with narrow size-distribution (standard deviation: 0.5–0.6 nm) supported on both hydroxylated (Fe_OH) and dehydrated iron oxide (Fe_O) have been prepared by either deposition-precipitation (DP) or colloidal-deposition (CD) methods. Different structural and textural characterizations were applied to the dried, calcined and used gold-iron oxide samples. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) showed high homogeneity in the supported Au nanoparticles. The ex situ and in situ X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) characterization monitored the electronic and short-range local structure of active gold species. The synchrotron-based in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), together with the corresponding temperature-programmed reduction by hydrogen (H2-TPR), indicated a structural evolution of the iron-oxide supports, correlating to their reducibility. An inverse order of catalytic activity between DP (Au/Fe_OH < Au/Fe_O) and CD (Au/Fe_OH > Au/Fe_O) was observed. Effective gold-support interaction results in a high activity for gold nanoparticles, locally generated by the sintering of dispersed Au atoms on the oxide support in the DP synthesis, while a hydroxylated surface favors the reactivity of externally introduced Au nanoparticles on Fe_OH support for the CD approach. This work reveals why differences in the synthetic protocol translate to differences in the catalytic performance of Au/FeOx catalysts with very similar structural characteristics in CO oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...