Near-infrared absorbing polymer nano-particle as a sensitive contrast agent for photo-acoustic imaging†
Abstract
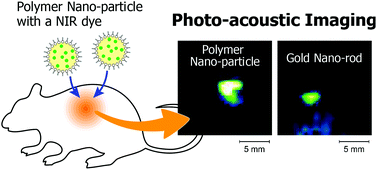
Polymer nano-particles (PNPs) with a near-infrared (NIR) light absorption were prepared by the nano-emulsion method to develop contrast agents for photo-acoustic (PA) imaging. The PNP containing silicon naphthalocyanine showed a high absorption coefficient up to 1010 M−1 cm−1. This is comparable to plasmonic gold nano-particles, which have been studied as PA contrast agents. For the PNP larger than 100 nm, the enhancement of the PA signal was observed compared to the gold nano-particle with a similar absorption coefficient and size. In the case of the PNP, the heat by the light absorption is confined in the particle due to the low thermal diffusivity of polymer materials. We showed that the strong thermal confinement effect of PNP results in the enhancement of the efficiency of the PA signal generation and that the PA intensity can be enhanced by the increase of the Grüneisen parameter of the matrix polymer of PNP. The PA signal from the PNP of poly(methyl methacrylate) was 9-fold larger than that of gold nano-particles with the same absorption coefficient. We demonstrated that in the in vivo PA imaging the detection limit of PNP was of the order of 10−13 M. The NIR absorbing PNP will be a promising candidate of a sensitive contrast agent for PA imaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...