Superlattice assembly of graphene oxide (GO) and titania nanosheets: fabrication, in situ photocatalytic reduction of GO and highly improved carrier transport†
Abstract
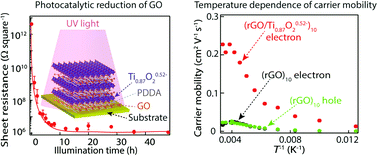
Two different kinds of two-dimensional (2D) materials, graphene oxide (GO) and titanium oxide nanosheets (Ti0.87O20.52−), were self-assembled layer-by-layer using a polycation as a linker into a superlattice film. Successful construction of an alternate molecular assembly was confirmed by atomic force microscopy and UV-visible absorption spectroscopy as well as X-ray diffraction analysis. Exposure of the resulting film to UV light effectively promoted photocatalytic reduction of GO as well as decomposition of the polycation, which are due to their intimate molecular-level contact. The reduction completed within 3 hours, bringing about a decrease of the sheet resistance by ∼106. This process provides a clean and mild route to reduced graphene oxide (rGO), showing advantages over other chemical and thermal reduction processes. A field-effect-transistor device was fabricated using the resulting superlattice assembly of rGO/Ti0.87O20.52− as a channel material. The rGO in the film was found to work as a unipolar n-type conductor, which is in contrast to ambipolar or unipolar p-type behavior mostly reported for rGO films. This unique property may be associated with the electron doping effect from Ti0.87O20.52− nanosheets. A significant improvement in the conductance and electron carrier mobility by more than one order of magnitude was revealed, which may be accounted for by the heteroassembly with Ti0.87O20.52− nanosheets with a high dielectric constant as well as the better 2D structure of rGO produced via the soft photocatalytic reduction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...