Drastic nickel ion removal from aqueous solution by curcumin-capped Ag nanoparticles†
Abstract
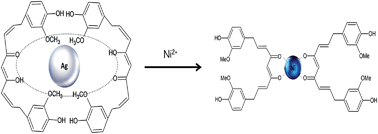
A completely green synthesis protocol has been adopted to obtain silver nanoaggregates capped by the natural compound (1E, 6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-diene), also known as curcumin. The synthesis has been monitored by infrared, Raman, visible and fluorescence spectroscopies. Characterization confirms that curcumin reduces and caps the nanoparticles, and such a procedure allows its solubility in water and drastically increases curcumin stability. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)/curcumin complex has been dispersed in a water solution containing a known nickel ion concentration. After three days, a grey precipitate is observed and nickel concentration in the solution is reduced by about 70%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...