Mucus barrier-triggered disassembly of siRNA nanocarriers†
Abstract
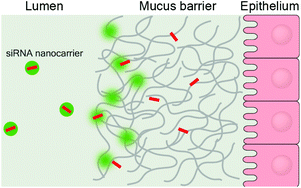
The mucus overlying mucosal epithelial surfaces presents not only a biological barrier to the penetration of potential pathogens, but also therapeutic modalities including RNAi-based nanocarriers. Movement of nanomedicines across the mucus barriers of the gastrointestinal mucosa is modulated by interactions of the nanomedicine carriers with mucin glycoproteins inside the mucus, potentiated by the large surface area of the nanocarrier. We have developed a fluorescence activation-based reporter system showing that the interaction between polyanionic mucins and the cationic chitosan/small interfering RNA (siRNA) nanocarriers (polyplexes) results in the disassembly and consequent triggered release of fluorescent siRNA. The quantity of release was found to be dependent on the molar ratio between chitosan amino groups and siRNA phosphate groups (NP ratio) of the polyplexes with a maximal estimated 48.6% release of siRNA over 30 min at NP 60. Furthermore, a microfluidic in vitro model of the gastrointestinal mucus barrier was used to visualize the dynamic interaction between chitosan/siRNA nanocarriers and native purified porcine stomach mucins. We observed strong interactions and aggregations at the mucin–liquid interface, followed by an NP ratio dependent release and consequent diffusion of siRNA across the mucin barrier. This work describes a new model of interaction at the nanocarrier–mucin interface and has important implications for the design and development of nucleic acid-based nanocarrier therapeutics for mucosal disease treatments and also provides insights into nanoscale pathogenic processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...