Facile graphene n-doping by wet chemical treatment for electronic applications†
Abstract
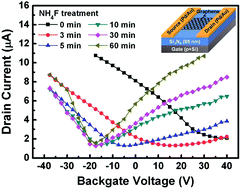
We report a post-synthetic n-doping method for chemical-vapor-deposition (CVD) grown graphene using wet chemical processing. An ammonium fluoride solution was found effective in converting pristine hole doping into electron doping in addition to the mobility improvement of charge carriers. We verified the doping by electrical measurements, Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses and suggest that the mechanism of n-doping is electrostatic doping by ionic physisorption of ammonium ions on the graphene surface. This simple chemical doping method provides a facile and robust route to n-doping of large area graphene for the realization of high performance graphene-based electronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...