Stem-loop DNA-assisted silicon nanowires-based biochemical sensors with ultra-high sensitivity, specificity, and multiplexing capability†
Abstract
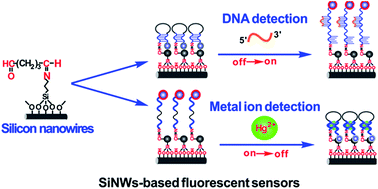
A class of stem-loop DNA-assisted silicon nanowires (SiNWs)-based fluorescent biosensor is presented in this report. Significantly, the sensor enables rapid and sensitive detection of DNA targets with a concentration as low as 1 pM. Moreover, the large planar surface of SiNWs facilitates simultaneous assembly with different DNA strands, which is favorable for multiplexed DNA detection. On the other hand, the SiNWs-based sensor is highly efficacious for detecting heavy metal ions. Mercury ions (Hg2+) of low concentrations (e.g., 5 pM) are readily identified from its mixture with over 10 kinds of interfering metal ions, even in real water samples. Given that SiNWs can be fabricated in a facile, reproducible and low-cost manner, this kind of SiNWs-based high-performance sensor is expected to be a practical analytical tool for a variety of biological and environment-protection applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...