Preparation and characterization of multi stimuli-responsive photoluminescent nanocomposites of graphene quantum dots with hyperbranched polyethylenimine derivatives†
Abstract
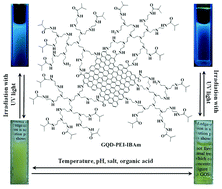
Oxidized graphene sheets (OGS) were treated with a hyperbranched polyethylenimine (PEI) under hydrothermal conditions to generate nanocomposites of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) functionalized with PEI (GQD–PEIs). The influence of the reaction temperature and the PEI/OGS feed ratio on the photoluminescence properties of the GQD–PEIs was studied. The obtained GQD–PEIs were characterized by TEM, dynamic light scattering, elemental analysis, FTIR, zeta potential measurements and 1H NMR spectroscopy, from which their structural information was inferred. Subsequently, isobutyric amide (IBAm) groups were attached to the GQD–PEIs through the amidation reaction of isobutyric anhydride with the PEI moieties, which resulted in GQD–PEI–IBAm nanocomposites. GQD–PEI–IBAm was not only thermoresponsive, but also responded to other stimuli, including inorganic salts, pH, and loaded organic guests. The cloud point temperature (Tcp) of aqueous solutions of GQD–PEI–IBAm could be modulated through changing the number of IBAm units in GQD–PEI–IBAm, by varying the type and concentration of the inorganic salts and loaded organic guests, or by varying the pH. All the obtained GQD–PEI–IBAm nanocomposites were photoluminescent, and their maximum emission wavelengths were not influenced by outside stimuli. Their emission intensities were influenced a little or negligibly by pH, traditional salting-out anions (Cl− and SO42−), and the relatively polar aspirin guest. However, the traditional salting-in I− anion and the more hydrophobic 1-pyrenebutyric acid (PBA) guest could effectively quench their fluorescence. 2D NOESY 1H NMR spectra verified that GQD–PEI–IBAm accommodated the relatively polar aspirin guest using the PEI–IBAm shell, but adsorbed the relatively hydrophobic PBA guest through the nanographene core. The release rate of the guest encapsulated by the thermoresponsive GQD is different below and above Tcp.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...