Sinapinic acid-directed synthesis of gold nanoclusters and their application to quantitative matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry†
Abstract
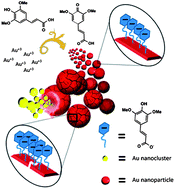
Core etching of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) into smaller-sized clusters is a classic method for fabricating gold nanoclusters (AuNCs). The top down-based synthesis of AuNCs includes two steps: (i) reducing the Au3+ precursor solution to generate AuNPs in the presence of protecting ligands and (ii) core etching of the formed AuNPs into the AuNCs via ligand exchange. For the first time, this paper describes a one-step approach for preparing AuNCs using a top down approach. The sinapinic acid (SA)-induced formation of the AuNCs involved a three-step reaction process. First, large AuNPs (>200 nm) were quickly formed after mixing SA and the Au3+ precursor solution. Second, excess SA molecules self-assembled on the NP surface, and large AuNPs were etched to small AuNPs via electrostatic repulsion between the neighboring SA molecules. Finally, SA-induced core etching of the AuNPs resulted in the formation of the AuNCs within 70 min. Furthermore, we showed that the presence of the AuNCs in SA was capable of suppressing crystal growth and eliminating the coffee-ring effect. Thus, proteins can be successfully quantified using the SA–AuNCs as matrices for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Compared with using SA as matrices, the SA–AuNCs offered substantial advantages for improving shot-to-shot reproducibility and enhancing the ionization efficiency of proteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...