Correlation of photobleaching, oxidation and metal induced fluorescence quenching of DNA-templated silver nanoclusters†
Abstract
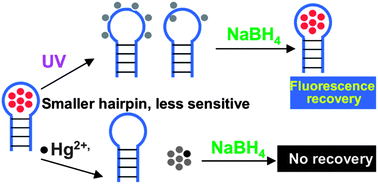
Few-atom noble metal nanoclusters have attracted a lot of interest due to their potential applications in biosensor development, imaging and catalysis. DNA-templated silver nanoclusters (AgNCs) are of particular interest as different emission colors can be obtained by changing the DNA sequence. A popular analytical application is fluorescence quenching by Hg2+, where d10–d10 metallophilic interaction has often been proposed for associating Hg2+ with nanoclusters. However, it cannot explain the lack of response to other d10 ions such as Zn2+ and Cd2+. In our effort to elucidate the quenching mechanism, we studied a total of eight AgNCs prepared by different hairpin DNA sequences; they showed different sensitivity to Hg2+, and DNA with a larger cytosine loop size produced more sensitive AgNCs. In all the cases, samples strongly quenched by Hg2+ were also more easily photobleached. Light of shorter wavelengths bleached AgNCs more potently, and photobleached samples can be recovered by NaBH4. Strong fluorescence quenching was also observed with high redox potential metal ions such as Ag+, Au3+, Cu2+ and Hg2+, but not with low redox potential ions. Such metal induced quenching cannot be recovered by NaBH4. Electronic absorption and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...