Ascorbic-acid-assisted growth of high quality M@ZnO: a growth mechanism and kinetics study†
Abstract
We present a general route for synthesizing M@ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) by using ascorbic acid (AA) to induce deposition of ZnO on various shaped and structured cationic-surfactant-capped NP surfaces (noble, magnetic, semiconductor, rod-like, spherical, cubic, dendrite, alloy, core@shell). The results show that the complexing (AA and Zn2+) and cooperative effects (AA and CTAB) play important roles in the formation of polycrystalline ZnO shells. Besides, the growth kinetics of M@ZnO was systematically studied. It was found that the slow growth rate favors the successful formation of uniform core@ZnO NPs with relatively loose shells. An appropriate growth rate allows achieving high quality M@ZnO NPs with dense shells. However, very fast growth causes significant additional nucleation and the formation of pure ZnO NPs. This general method is suitable for preparing M@ZnO using seed NPs prepared in both water and organic phases. It might be an alternative route for functionalizing NPs for bioapplications (ZnO is biocompatible), modulating material properties as designed, or synthesizing template materials for building other nanostructures.
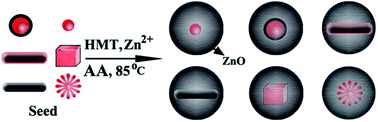

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...