Highly reversible lithium storage in Si (core)–hollow carbon nanofibers (sheath) nanocomposites†
Abstract
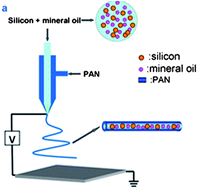
A favorable Si (core)–hollow carbon nanofiber (sheath) nanocomposite, was synthesized by a coaxial electrospinning technique. As a potential anode material for LIBs, this composite displays a high reversible capacity of 1300 mA h g−1 even after 80 cycles at 0.5 C. It also exhibits a reversible discharge capacity as high as 700 mA h g−1 when cycled at 3 C. This makes the Si–C composite a promising candidate for use as an anode material in lithium ion batteries. Beyond that, coaxial

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...