Crystal splitting and enhanced photocatalytic behavior of TiO2rutile nano-belts induced by dislocations†
Abstract
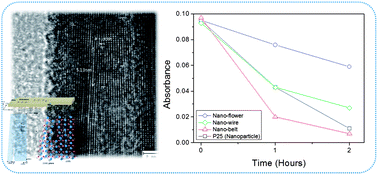
Crystal splitting and enhanced photocatalytic activities caused by implied dislocations were observed in hierarchical TiO2 nano-architectures prepared by one-pot

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...