Formation of nanostructured porous Cu–Au surfaces: the influence of cationic sites on (electro)-catalysis†
Abstract
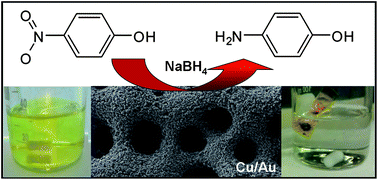
The fabrication of nanostructured bimetallic materials through electrochemical routes offers the ability to control the composition and shape of the final material that can then be effectively applied as (electro)-catalysts. In this work a clean and transitory hydrogen bubble templating method is employed to generate porous Cu–Au materials with a highly anisotropic nanostructured interior. Significantly, the co-electrodeposition of copper and gold promotes the formation of a mixed bimetallic oxide surface which does not occur at the individually electrodeposited materials. Interestingly, the surface is dominated by Au(I) oxide species incorporated within a Cu2O matrix which is extremely effective for the industrially important (electro)-catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. It is proposed that an aurophilic type of interaction takes place between both oxidized gold and copper species which stabilizes the surface against further oxidation and facilitates the binding of 4-nitrophenol to the surface and increases the rate of reaction. An added benefit is that very low gold loadings are required typically less than 2 wt% for a significant enhancement in performance to be observed. Therefore the ability to create a partially oxidized Cu–Au surface through a facile electrochemical route that uses a clean template consisting of only hydrogen bubbles should be of benefit for many more important reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...