Visible–NIR photodetectors based on CdTe nanoribbons†
Abstract
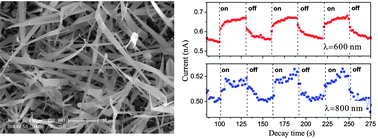
Zinc blende-structured CdTe nanoribbons (NRs) were synthesized for the first time via a two-step process. The electronic, transport, and photoconductive properties of the CdTe NRs were studied systematically. It was revealed that the CdTe NRs showed p-type conductivity, and presented significant photoresponses to visible–NIR (400–800 nm) irradiation with high responsivity and gain. The contribution of the factors such as surface states of NRs, channel length, light intensity, and working bias voltage to the photoresponse characteristics of CdTe NR photodetectors were discussed. Moreover, single CdTe NR-based visible–NIR photodetectors were also demonstrated to have high stability and reliability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...