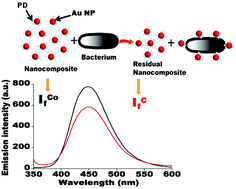
Rapid, simple and sensitive detection of bacterial contamination is critical for safeguarding public health and the environment. Herein, we report an easy method of detection as well as enumeration of the bacterial cell number on the basis of fluorescence quenching of a non-antibacterial fluorescent nanocomposite, consisting of paracetamol dimer (PD) and Au nanoparticles (NPs), in the presence of bacteria. The composite was synthesized by reaction of paracetamol (p-hydroxyacetanilide) with HAuCl4. The Au NPs of the composite were characterized using UV-Vis spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction and selected area electron diffraction analysis. The paracetamol dimer in the composite showed emission peak at 435 nm when excited at 320 nm. The method successfully detected six bacterial strains with a sensitivity of 100 CFU mL−1. The Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria quenched the fluorescence of the composite differently, making it possible to distinguish between the two. The TEM analysis showed interaction of the composite with bacteria without any apparent damage to the bacteria. The chi-square test established the accuracy of the method. Quick, non-specific and highly sensitive detection of bacteria over a broad range of logarithmic dilutions within a short span of time demonstrates the potential of this method as an alternative to conventional methods.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...