Light energy harvesting with nano-dipoles
Abstract
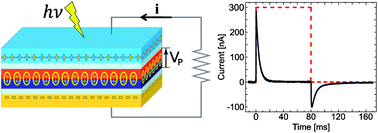
We propose a new approach for converting light energy into electrical energy, based on the photogeneration of nano-dipoles at donor–acceptor interfaces. The nano-dipoles are oriented in space so as to contribute to a collective polarization that induces a potential difference across the material, sandwiched between electrodes. A current is detected in the external circuit upon illumination. Such a device would exploit many advantages of organic semiconductors and get rid of the main limitation, namely transport. We provide a proof of concept and we discuss the ideal limit of the device based on numerical simulations. This provides design guidelines to the achievement of best performances. Simulations show that the proposed device can be an appealing opportunity with giant conversion efficiency provided some technological issues are overcome.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...